Search Mode Filters
Refine your search results with filters. Standard filters limit results to showing only records that contain one or more of the search terms in their Title, Learned Terms, Keywords, or Content Text. Advanced filters can leverage any available content record metadata field, including custom meta data fields (e.g., Language, Expiration Date, etc.).
Specify Search Filters
To refine your search results, use the Filters tab in the left navigation panel. You can refine your search results by the following categories of standard filters: properties and permissions; custom metadata; keywords and terms; stats and history; review jobs; and translations.
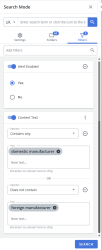
- Once you've selected existing slices or entered custom terms, select the Filters tab to access search filters.
- Use the Add Filters field to either select or search for specific filers.
- To select a filter, click into the Add Filters field and select one or more filters to apply.
- To search for a filter, enter text into the Add Filters field the Search
 button or press Enter.
button or press Enter.
- Configure the filters with the required inputs to apply them to the search results. Select the appropriate operator(s) for each filter from the dropdown list. With a wide range of operators available for each field type, the filter values you provide can be very flexible or specific as you need. The filter types and the available operators are described below:
- Text Columns: Select either Contains All, Contains Any, Matches Any, Matches Exactly, Starts with, Ends with, Is Empty, Is Not Empty, or Does Not Contain from the Operator dropdown menu. The Contains All, Contains Any, Does Not Contain, and Matches Any operators allows you to enter more than one value by pressing the Enter key after each value. The Starts with and Ends with operators allow you to enter a text value to find. The Is Empty and Is Not Empty operators do not require a value.
- Numeric: Select either Equals, Greater than, Less than, Greater than or equal to, Less than or equal to, Not equal to, Between, Matches Any, Matches any or is empty, Is empty, or Is not empty from the dropdown menu. In the corresponding field, enter the required numbers. For example, for the Revision field, if you select the Matches Any operator then you will be presented with a text box to enter multiple version numbers.
- Date: Select either On, After, Before, Between, Is empty, or Is not empty from the dropdown menu. In the corresponding field, click the Calendar
 icon to select the required date(s). For example, for the field Date Expires if you select the operator Between, then you will be presented with From and To date fields to select the date range. All the records that are scheduled to expire in that range are filtered.
icon to select the required date(s). For example, for the field Date Expires if you select the operator Between, then you will be presented with From and To date fields to select the date range. All the records that are scheduled to expire in that range are filtered.
- Apply one or more conditions to a filter by selecting Add Condition from the More Options
 menu. To remove a condition from a filter, click the Remove icon
menu. To remove a condition from a filter, click the Remove icon  next to the desired condition.
next to the desired condition. Example: Starts with X OR starts with Y. Contains All (A, B, C) OR contains all (X, Y, Z). Date > X OR is empty.
- Click Search. The filters are applied to further refine the search results.
Tip: To apply suggested filters, see Suggested Filters.
Note: Once a search filter is selected, a blue checkmark will appear next to the dropdown menu.
Note: You can activate or deactivate a filter by using the toggle switch available on each filter. Click the Remove icon ![]() to remove a filter with a single condition. To remove a filter with multiple conditions, select Remove Filter from the More Options
to remove a filter with a single condition. To remove a filter with multiple conditions, select Remove Filter from the More Options ![]() menu.
menu.
Filter types
Limit you search results to include only content records of a specific file format such as Microsoft Word or Excel, or content type such as Slide, File, Q/A, or item.
You can limit your search result to content records based on details like the number of times used (Times Used Counter), links (Linked), a translation parent record (Translation parent ID), and the translation status (Translation Status).
Tip: "Times Used Counter" is a cumulative count of the record's use since creation. Please be aware that "Times Used" always displays the cumulative count of the record's use since its creation, not the number of times used from a date or between dates.
You can search for content based on the user(s) who created, owned, managed, last used or modified, or checked out the content record.
Choose the appropriate filter (on, before, after, or between), then use the calendar icon to navigate to the appropriate date the content was created, last modified, checked out/in, expired or last used.
Tip: The "Date created" is the date of the Content record creation (Month, Month/Year, Quarter, Quarter/Year, Year, Day of Week, Week). "Date Last Modified" is the latest date of changes to the content record properties. The "last modified" is the latest revision date or an update to the properties. "Date checked in" is the recent check-in date (Month, Month/Year, Quarter, Quarter/Year, Year, Day of Week, Week). "Date checked out" is the latest check-out date (Month, Month/Year, Quarter, Quarter/Year, Year, Day of Week, Week). "Expired" means this content record is currently expired. "Date Last Used" is the date of the latest use of the content record.
If your instance of Upland Qvidian has been configured with custom metadata, you can search for records based on their metadata values. The parameters shown on the Custom Metadata filter reflect how the metadata was configured for your specific Upland Qvidian instance.
Suggested Filters
Qvidian can suggest filters based on content records’ custom metadata. With suggested filters, you can refine results more efficiently to locate the most relevant answers faster. When you apply a suggested filter to search results, Qvidian automatically adds the filter to the “Advanced Filters” list so you can enable/disable the filter easily in the future.
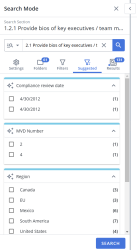
Example: If Qvidian detected that records in your results had the custom metadata field “Region,” Qvidian would suggest the “Region” filter. From there, the user could pick from the regions shown to refine their search results. If Qvidian detected that records in your results had the custom metadata field “Language,” Qvidian would suggest the “Language” filter. From there, the user could pick from the languages shown to refine their search results.
Note: The following suggested filter Global Settings are enabled by default: "EnableLibraryContentSuggestedFilters", "LibraryContentSuggestedFiltersMaxOptions", and "LibraryContentSuggestedFiltersMinOptions". The following user permission must be enabled to use suggested filters: "Allow User to use Search Mode in Projects".
- Perform a search on a particular slice/cell or enter a search term directly into the Search field.
- Select the Suggested tab to view any suggested filters.
- Select the checkboxes of any desired suggested filters, which are organized into their respective filter categories.
- Click Search. When you apply a suggested filter to search results, Qvidian automatically adds the filter to the Advanced Filters list so you can enable/disable the filter easily in the future.
Tip: If suggested filters are available for a particular search, a blue dot icon will appear on the Suggested tab.